What Is Colocation Hosting? Complete Guide for 2025
7 min read - September 11, 2025
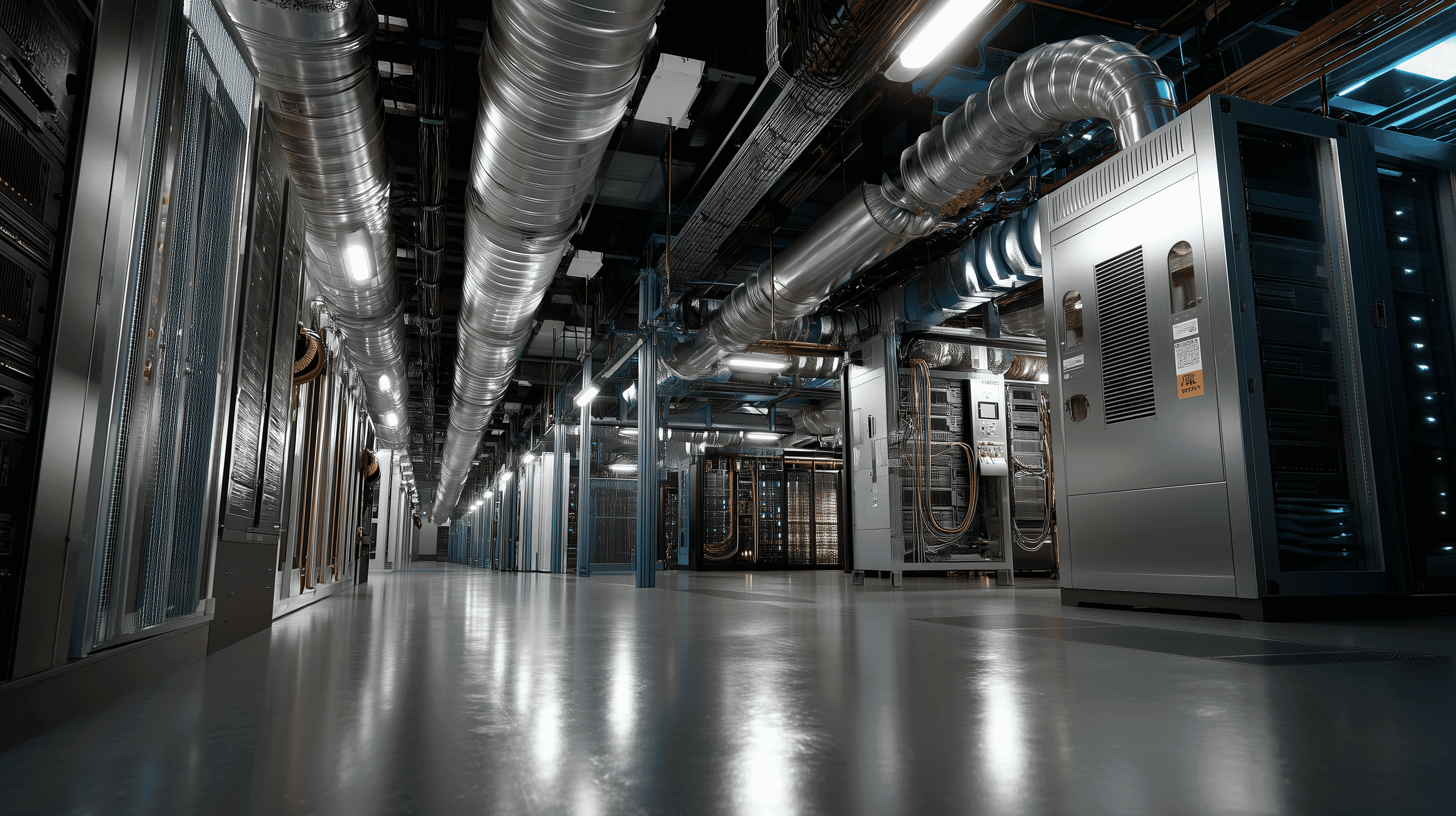
Colocation hosting offers businesses control over their servers while providing essential infrastructure support, making it ideal for high-performance workloads.
What Is Colocation Hosting? Complete Guide for 2025
Colocation hosting lets you place your own servers in a third-party data center. You maintain full control over your hardware and software, while the provider handles the physical infrastructure like power, cooling, security, and internet connectivity. This setup combines high performance, reliability, and cost savings, making it ideal for businesses with demanding workloads like AI, big data, and financial services.
Key Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Avoid building your own data center; pay predictable monthly fees instead.
- Scalability: Start small and expand as needed, from single racks to private cages.
- Reliability: Redundant power, cooling, and network connections ensure uptime.
- Security: Advanced physical and network security measures protect your equipment.
- Customization: Use your own hardware and configure it to meet your specific needs.
Why It Matters in 2025:
- Supports high-performance computing for AI and data-heavy tasks.
- Fits hybrid cloud strategies by combining private hardware with cloud scalability.
- Meets strict compliance standards for industries like healthcare and finance.
Colocation is a practical solution for businesses looking to balance control, performance, and cost efficiency in their IT infrastructure.
Benefits and Use Cases of Colocation Hosting
Cost Savings and Scalability
Colocation hosting offers a cost-effective alternative to building and maintaining your own data center. Instead of covering hefty upfront expenses for power, cooling, and security infrastructure, businesses pay a predictable monthly fee. This shift turns significant capital investments into manageable operational costs.
One of colocation's biggest draws is its scalability. Businesses can start small - perhaps with just a single rack unit - and expand as their needs grow. Whether you need a few racks or an entire private cage, colocation adapts to your growth without requiring oversized infrastructure from the start. This flexibility ensures you’re neither overcommitting resources nor outgrowing your setup too quickly.
Another advantage is access to bulk electricity rates that individual businesses typically can’t secure. Colocation facilities also feature redundant power systems, including uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup generators - critical infrastructure that would otherwise cost tens of thousands of dollars to implement on your own.
The cost-sharing model extends to other essentials like cooling systems, fire suppression, and on-site security. By pooling resources with other tenants, you gain access to professional-grade facilities at a fraction of the cost of building them independently. This combination of affordability, reliability, and advanced security makes colocation an appealing choice for businesses of all sizes.
Reliability and Security
Colocation facilities are built with redundancy in mind, ensuring uptime even during unforeseen events. Power systems often include dual utility feeds, battery backups, and diesel generators capable of running for days. This level of preparation protects your servers from outages, even during major grid failures.
Cooling infrastructure is equally robust. Professional colocation centers maintain precise temperature and humidity levels using redundant HVAC systems and optimized airflow designs like hot aisle/cold aisle configurations. Without these measures, servers could overheat and fail within minutes, making cooling a critical component of reliable operations.
Security is another cornerstone of colocation hosting. These facilities use advanced physical security measures, including biometric access controls, 24/7 on-site personnel, surveillance systems, and man-trap entryways. Some even feature reinforced walls and bulletproof glass to withstand natural disasters or other threats.
To minimize downtime, colocation centers offer multiple data paths. If one network provider encounters an issue, traffic is automatically rerouted through alternative connections, keeping your operations running smoothly and avoiding costly interruptions.
Use Cases for High-Performance and AI Workloads
Colocation’s benefits extend far beyond cost and reliability, making it a strategic choice for demanding workloads.
For businesses running artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications, colocation provides the infrastructure needed to handle these resource-intensive tasks. GPU servers, essential for AI and ML, generate significant heat and require high power levels. Colocation facilities are equipped with the cooling and electrical systems necessary to run these servers continuously and efficiently.
Gaming companies and real-time applications also thrive in colocation environments. Low-latency network connections are crucial for delivering smooth performance, especially when milliseconds can make or break user experiences. With direct access to major internet exchanges, colocation ensures faster, more reliable connections.
Data-heavy operations like video rendering, scientific computing, and large-scale data analysis benefit from colocation’s ability to support custom hardware setups. Whether it's NVMe storage arrays or high-memory configurations, colocation allows businesses to design systems tailored to their needs - something that cloud providers may not offer or that could be prohibitively expensive for long-term use.
Financial services companies leverage colocation for high-frequency trading. Proximity to major exchanges and dedicated network connections provide the low-latency environment needed to execute trades at lightning speed, directly impacting profitability.
Colocation also plays a key role in backup and disaster recovery. By hosting secondary infrastructure in geographically separate facilities, businesses can ensure continuity even if their primary location experiences issues. This approach gives companies greater control over recovery processes compared to relying solely on cloud-based solutions.
How Colocation Hosting Works
The Colocation Setup Process
Setting up your servers in a colocation facility is a straightforward process. It all begins with your hardware - servers, networking gear, storage devices, and any specialized components your applications might need. You’re responsible for purchasing or configuring this equipment.
Once your hardware is ready, it’s time to arrange delivery to the data center. Most facilities are equipped with loading docks and dedicated receiving areas to safely handle server equipment. The colocation provider will typically schedule a delivery window and assign technical staff to assist with the initial setup.
During installation, technicians will mount your servers in the assigned rack space, connect power cables to the facility’s power distribution units, and establish network connections. You’ll also receive essential details such as IP addresses, network configurations, and remote access credentials.
From there, the colocation provider takes over the foundational infrastructure while you retain full control over your hardware and applications.
Infrastructure Features and Provider Responsibilities
Colocation providers focus on maintaining the critical infrastructure that supports your servers, leaving you free to manage your hardware and software. Here’s what they handle:
- Power redundancy: Facilities typically offer multiple utility feeds, battery backup systems, and diesel generators. Many operate with at least N+1 redundancy, ensuring backup systems are in place for every critical component.
- Climate control: Data centers maintain optimal conditions, keeping temperatures between 68°F and 72°F (20°C to 22°C) and humidity levels around 45-55%. Precision air conditioning and strategic airflow prevent overheating and equipment damage.
- Network connectivity: Colocation facilities are often carrier-neutral, giving you access to multiple internet service providers and exchanges. This setup provides redundancy and allows you to choose the best connectivity options for your needs.
- Physical security: Facilities are monitored 24/7 and use layered access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can access your equipment.
The responsibilities are clearly divided: the provider manages the building, power, cooling, and basic network infrastructure, while you oversee your servers, operating systems, applications, and data. This setup ensures you maintain full control over your IT environment without the burden of managing the physical facility.
Steps to Get Started with Colocation
Getting started with colocation requires planning and preparation. Here’s how to set yourself up for success:
- Audit your hardware: Make sure your equipment is compatible with standard 19-inch server racks. Colocation facilities typically use rack units (U), where 1U equals 1.75 inches of vertical space. Also, document your power needs, including any special electrical requirements.
- Plan your network: Identify your bandwidth needs and decide if you’ll require dedicated connections to specific carriers or cloud providers. Many businesses benefit from hybrid setups that combine colocation with cloud services, so keep this in mind when designing your network architecture.
- Set up remote management tools: Before shipping your equipment, configure tools like IPMI or iDRAC to monitor server health, performance, and temperature remotely. You may also need to set up VPN access for secure remote management.
- Document everything: Record server configurations, network settings, and key technical contacts. Share this information with the colocation provider’s technical team, as they often offer remote hands services for tasks like rebooting servers or replacing components.
- Budget for ongoing costs: Beyond monthly colocation fees, account for bandwidth overages, remote hands services, and potential hardware replacements. Detailed documentation and planning can help minimize additional expenses.
- Start small: Consider a pilot deployment with a portion of your infrastructure to test the facility’s performance and support quality. This trial run will help you fine-tune your procedures before moving critical systems.
Colocation Hosting Trends for 2025
New Trends in Colocation Hosting
The colocation industry is undergoing rapid changes as businesses push for more computing power and tailored infrastructure. High-density racks have become the norm, allowing companies to pack more processing capability into smaller spaces. This not only cuts down on space-related costs but also boosts overall performance. A big reason for this shift is the growing demand from AI and machine learning workloads, which require specialized hardware. These systems generate significant heat, prompting providers to adopt advanced cooling and power distribution technologies. The result? Enhanced performance and a step toward more efficient operations.
Another game-changer is edge computing. With the need to process data closer to users, smaller facilities in less centralized locations are popping up to meet this demand. This distributed approach helps reduce latency for applications like autonomous vehicles, IoT devices, and real-time analytics. At the same time, the rise of hybrid cloud architectures is reshaping colocation design. Many providers now offer direct connections to multiple cloud platforms, making it easier for businesses to move between on-premises servers and cloud environments. This not only boosts performance but also tightens security.
Sustainability and Green Initiatives
Colocation providers are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly practices to minimize their environmental footprint. Efforts to improve energy efficiency are front and center, with innovations in cooling leading the charge. Liquid and immersion cooling systems, for example, are helping manage the heat from high-density computing while using less energy and operating more quietly. Renewable energy is also gaining traction, with providers signing long-term renewable energy agreements or installing on-site renewable systems to reduce dependence on traditional power grids. Another smart move? Repurposing waste heat, which boosts efficiency while cutting down on environmental impact.
Bandwidth and Resource Management Tools
Today's colocation facilities are smarter than ever, thanks to advanced monitoring and automation tools. Real-time analytics now offer granular insights into power usage, temperature, humidity, and network performance - all the way down to individual servers. Predictive maintenance systems, powered by machine learning, can flag potential equipment issues before they cause downtime. Automated systems are also stepping up, dynamically adjusting power, cooling, and bandwidth based on real-time needs.
Software-defined networking (SDN) and API-driven tools give businesses more control, enabling them to tweak network configurations and integrate monitoring into their existing IT systems. Digital twin technology is another exciting development. By creating virtual models of physical infrastructure, administrators can test scenarios - like adding new equipment or tweaking cooling systems - before making real-world changes. These tools are essential for keeping up with the demands of modern applications, from AI-driven tasks to real-time data processing.
Optimizing Performance in Colocation Environments
For enterprises relying on colocation to power high-performance and AI-driven operations, fine-tuning performance is the next logical step after leveraging the robust infrastructure these facilities provide.
Maximizing Server Performance
To get the most out of colocation, your hardware needs to match your workload. AI and machine learning applications, for instance, thrive on high-performance processors with multiple cores and accelerators like GPUs or TPUs. When choosing servers, don’t overlook thermal design power (TDP) - higher ratings mean increased cooling demands and can impact rack density, which translates to higher costs.
Network connectivity is another key factor. While most colocation providers offer various bandwidth tiers, it’s critical to align your choice with your application's needs. For latency-sensitive tasks, direct fiber connections and redundant network paths are a must. Data-heavy workloads benefit from providers offering 10 Gbps or even 100 Gbps connections with minimal contention.
The way you configure storage also plays a major role in performance. NVMe SSDs are a game-changer for workloads requiring fast data access, like database servers. For mixed-use cases, a tiered storage setup - combining high-speed SSDs for active data with larger, slower drives for archival storage - can strike the right balance between speed and capacity.
Memory optimization is equally important, especially when running multiple virtual machines or containers. DDR5 memory stands out for its higher bandwidth and lower power consumption compared to older memory types. To ensure smooth performance during traffic spikes, plan for a memory overhead of 20-30% above your baseline requirements.
Once your hardware and storage are optimized, it’s time to focus on managing bandwidth and resources effectively.
Managing Bandwidth and Resources
Bandwidth monitoring is essential for understanding how your network is being used. While colocation providers typically offer basic traffic graphs, more detailed insights come from custom monitoring tools. These tools can track usage by protocol, application, or even individual servers, helping you spot inefficiencies and avoid unexpected overage fees.
If your traffic patterns allow, consider burstable bandwidth plans to save costs. These plans let you pay for a lower committed rate while still accessing higher speeds during peak times. Analyze your 95th percentile usage to determine if this model works for you - if your usage rarely exceeds the burst threshold, it could be a cost-effective option.
Scaling resources in colocation environments requires careful planning since you can’t add hardware instantly, as you would in the cloud. Use monitoring tools to track CPU, memory, and storage utilization, setting alerts at 70%, 80%, and 90% thresholds. This gives you enough lead time to order and deploy additional resources before performance suffers.
Power management is another area to address, especially as server density increases. Modern servers often support dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS), which adjusts processor speeds based on workload demands. Enabling DVFS can cut power consumption by 15-25% during low-use periods without sacrificing performance when demand picks up.
Beyond these optimizations, robust remote management practices are critical for maintaining performance over time.
Best Practices for Remote Management
Out-of-band management tools like the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) are indispensable for remote monitoring and control. They allow you to access consoles, manage power, and monitor hardware health even if the main network is down. To ensure reliability, set up these systems on dedicated management networks separate from production traffic.
Secure remote access is another must. Use VPNs with multi-factor authentication and consider deploying jump servers or bastion hosts. This setup minimizes direct internet exposure while ensuring secure and reliable access for administrators.
Automated monitoring systems should track both hardware health and application performance. Configure alerts for issues like temperature spikes, fan failures, power supply problems, and disk errors to catch potential problems before they escalate. Focus on metrics that directly affect system responsiveness and throughput.
Disaster recovery planning is especially critical in colocation environments where you own the hardware. Keep current system images and configuration backups stored both on-site and off-site. Document step-by-step recovery procedures for different scenarios, from single-server failures to full facility outages, and test these plans quarterly to confirm they work as intended.
Finally, stay on top of firmware and security updates. Schedule updates during low-traffic periods and test them on non-production systems first. Maintain detailed change logs and have rollback procedures in place, as physical recovery operations in colocation environments can take significantly longer than in cloud setups.
FDC Colocation Solutions
FDC Servers brings over 23 years of expertise to the table, specializing in colocation services designed for data-intensive and AI-driven workloads. Their infrastructure is built to handle the rigorous demands of modern computing, including machine learning and other critical data operations.
What FDC Servers Offers
With 74 colocation locations worldwide, FDC Servers provides businesses with strategic options for placing their critical infrastructure. Their facilities are equipped to support high-density deployments, offering up to 22kW per rack - ideal for power-hungry setups like GPU clusters and high-performance computing systems. This ensures businesses can fully optimize their rack efficiency.
Bandwidth capacity is another standout feature. FDC Servers delivers IP transit services at 10, 100, and 400 Gbps, leveraging a diverse carrier mix that includes Comcast, NTT, TATA, GTT, Cogent, and local peering partners. This variety ensures redundancy and efficient global traffic routing and is included in Colocation services.
Security and compliance are a priority, with facilities adhering to SOC 2, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 standards. These certifications make FDC Servers a reliable choice for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
Why Choose FDC Servers?
Starting at $399 per month, FDC Servers offers transparent pricing with clear tiers based on power and bandwidth needs. They also provide 24/7 technical support, staffed by experts in high-performance hosting, ensuring businesses receive the assistance they require at any time.
Scalability is another key advantage. Businesses can start small and expand as their needs grow, thanks to flexible rack configurations and power options that allow for cost-effective scaling.
FDC Servers has a history of staying ahead of the curve, being among the first to offer servers with 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 100 Gbps port connections. This forward-thinking approach continues to benefit customers requiring advanced connectivity options.
Service Tier Overview
These tiered options allow businesses to match their colocation investment with their specific performance needs. Whether you're running a single high-performance server or managing a full rack for complex tasks, FDC Servers provides the flexibility and power to support your goals.
Conclusion
Main Takeaways
Colocation hosting delivers unmatched control, performance, and reliability by housing your servers in professional data centers, sparing you the hassle of building and maintaining your own facility.
By tapping into shared data center resources - such as cooling systems, backup power, and advanced security - you maintain complete control over your hardware and software configurations. This makes colocation ideal for demanding applications like AI, high-performance computing, and data-heavy operations. Plus, it’s a cost-efficient solution that grows with your business, allowing you to start small and scale up as needed, paying only for the resources you consume.
For businesses exploring colocation options in 2025, FDC Servers offers a powerful solution. With a presence in over 70 global locations, their colocation services can handle configurations of up to 22kW per rack. They also provide 24/7 technical support to ensure your systems run smoothly, making them a strong choice for high-performance server applications and AI workloads.
As companies seek the perfect balance between cloud convenience and dedicated control, colocation hosting stands out as a reliable and scalable option for securing the future of your IT infrastructure.
FAQs
What’s the difference between colocation hosting and owning your own data center?
Colocation hosting and owning a data center are two distinct approaches to managing IT infrastructure, each with its own set of responsibilities and costs. With colocation, you own the servers but lease space, power, and network connectivity in a facility operated by a third party. This setup lets you share essential resources like cooling systems and security measures with other tenants, which helps reduce operational expenses.
On the other hand, owning a data center puts you in charge of everything - maintenance, staffing, and all infrastructure needs. While this gives you complete control, it also means taking on significantly higher costs and management duties. Colocation offers a practical and adaptable option for businesses that want access to top-tier infrastructure without the heavy burden of owning and running an entire facility.
What should I look for in a colocation provider for AI and machine learning workloads?
When choosing a colocation provider for AI and machine learning tasks, focus on scalability, network performance, and reliability. You'll want a provider that can deliver high-speed, low-latency network connections to handle the massive data transfers these workloads require. It's also essential to find one that supports seamless scaling of resources - like GPUs and storage - to meet the demands of growing or fluctuating workloads.
Don't stop there. Check whether the provider has advanced cooling systems and high-density infrastructure to maintain the performance and stability of high-power servers. Equally important are strong security measures and uptime guarantees, ensuring your data stays protected and your operations run smoothly.
How does colocation hosting help with disaster recovery and backup planning?
Colocation hosting strengthens disaster recovery and backup plans by offering secure, off-site facilities to safeguard your essential systems and data. These facilities are equipped with redundant infrastructure, including uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and backup generators, which help keep operations running smoothly during unexpected disruptions.
By using colocation, companies can replicate their data across multiple geographically separated locations, allowing for swift recovery if the primary site experiences a failure. It also enables routine testing of backups and recovery processes, ensuring systems are ready to handle emergencies. This setup plays a critical role in maintaining business operations and protecting against data loss during catastrophic events.

How to install and use Redis on a VPS
Learn how to install and configure Redis on a VPS for optimal performance, security, and management in your applications.
9 min read - January 7, 2026
Monitoring your Dedicated server or VPS, what are the options in 2025?
12 min read - November 28, 2025

Have questions or need a custom solution?
Flexible options
Global reach
Instant deployment
Flexible options
Global reach
Instant deployment