How to Analyze IP Transit Traffic with NetFlow
8 min read - October 3, 2025

Learn how to effectively analyze IP transit traffic using NetFlow for improved network performance, security, and cost management.
How to Analyze IP Transit Traffic with NetFlow
NetFlow is a tool that provides detailed insights into network traffic, helping businesses manage performance, costs, and security. Here's a quick summary:
- What is NetFlow? A protocol developed by Cisco that collects and exports data about IP traffic flows, including source/destination IPs, ports, protocols, and traffic volume.
- Why use it? It helps monitor bandwidth usage, detect anomalies, and improve security by identifying unusual activity.
- Key benefits: Tracks traffic patterns, identifies top bandwidth consumers, aids in capacity planning, and enhances security by detecting threats like DDoS attacks.
- How to set it up: Configure NetFlow-enabled devices, set up collectors for data storage, and use analysis tools for actionable insights.
- Best practices: Use sampling rates for high-traffic networks, deploy multiple collectors for redundancy, and monitor both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic for full visibility.
NetFlow transforms raw traffic data into actionable insights, making it easier to optimize networks, detect security issues, and manage costs effectively.
Understanding Netlow
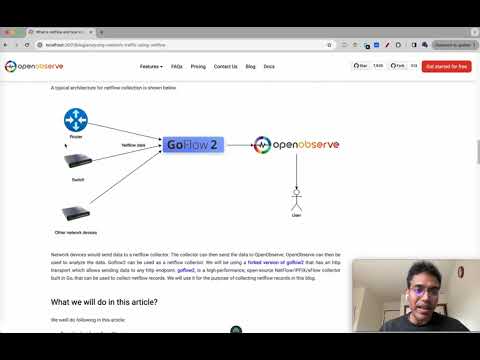
Understanding NetFlow: How to Analyze Network Traffic with OpenObserve
Setting Up NetFlow for IP Transit Monitoring
To monitor IP transit effectively with NetFlow, you'll need to configure your devices, set up collectors, and ensure your infrastructure can handle high volumes of flow data.
NetFlow Configuration Requirements
To get started, you'll need three key components: NetFlow-enabled devices, collectors, and analysis tools.
First, ensure your network includes NetFlow-capable devices. These devices generate flow records with minimal impact on performance. Most modern routers and switches support NetFlow or similar protocols like sFlow or IPFIX. For routers handling IP transit traffic, sufficient CPU and memory are crucial to manage flow sampling alongside routing tasks. In high-bandwidth environments - processing traffic in the range of multiple gigabits per second - dedicated monitoring hardware or robust software-based collectors are often necessary.
Next, set up a NetFlow collector. This component receives, stores, and processes the exported flow records. Collectors must have enough storage to retain historical data and support trend analysis. For networks with terabytes of monthly traffic, plan on using collectors with several terabytes of storage and fast disk I/O capabilities to handle the load effectively.
Finally, use analysis and visualization tools to make sense of the raw data. These tools transform flow records into actionable insights via dashboards, reports, and alerts. Choose tools based on your specific needs, whether you're focusing on bandwidth management, security, or cost control.
Once you have these components ready, you can enable and fine-tune NetFlow on your network devices.
How to Enable and Configure NetFlow
Configuring NetFlow starts with setting up your network devices to generate and export flow records.
- Interface-level configuration: Enable monitoring on the interfaces carrying IP transit traffic. Configure both ingress and egress monitoring to capture bidirectional traffic. Adjust the sampling rate based on your network size - smaller networks may use a rate like 1:100, while high-traffic networks might go up to 1:10,000.
- Flow export configuration: Specify where the flow data will be sent. Set up the NetFlow collector's IP address, UDP port (commonly 9995 or 2055), and export interval. Shorter intervals provide near real-time insights but increase network overhead and processing demands on collectors.
- Flow record templates: Define the content of each flow record. Standard NetFlow v5 templates include fields like source and destination IPs, ports, protocol details, packet counts, and byte volumes. For more flexibility, use NetFlow v9 or IPFIX to include additional fields such as MPLS labels, VLAN tags, or application-specific data.
- IPv6 flow monitoring: If your network supports IPv6, configure flow monitoring for both IPv4 and IPv6. Many networks operate in dual-stack environments, and failing to monitor IPv6 traffic can leave gaps in your visibility.
- BGP next-hop information: Add this context to help identify which upstream providers or peering connections are handling specific traffic flows. This is especially helpful for managing costs and troubleshooting performance issues in IP transit environments.
Once the basic settings are in place, you can apply best practices to optimize NetFlow performance in high-bandwidth scenarios.
Configuration Best Practices for High-Bandwidth Networks
For networks with heavy traffic, fine-tuning your NetFlow setup is essential to maintain accuracy and efficiency.
- Adjust sampling rates: In networks processing over 10 Gbps, use sampling rates between 1:1,000 and 1:10,000. This provides statistically meaningful data without overwhelming your collectors or impacting router performance.
- Deploy multiple collectors: Spread collectors across different regions to reduce the load on individual systems and ensure redundancy. This setup minimizes bandwidth usage on management networks and ensures critical monitoring data is always available.
- Aggregate flow data: To manage high traffic volumes, configure devices to aggregate flow data based on parameters like source/destination networks, protocols, or time intervals. This reduces the number of individual flow records while preserving key traffic patterns.
- Optimize export timing: Avoid data loss during peak traffic by setting export intervals appropriately. For dynamic networks, intervals of 30–60 seconds work well, while stable networks can use intervals of 5–10 minutes. Regularly check your collector's processing capacity to ensure it can handle peak export volumes.
- Set template refresh rates: For NetFlow v9 and IPFIX, refresh templates frequently enough to account for collector restarts or network interruptions. A good rule of thumb is every 1,000 flow records or every 30 minutes.
- Use QoS for NetFlow exports: Assign NetFlow export traffic to a dedicated Quality of Service (QoS) class with guaranteed bandwidth. This ensures your monitoring data reaches the collectors even during periods of network congestion, maintaining visibility when it's needed most.
Collecting and Processing NetFlow Data
Once the configuration is set, the next step is to focus on gathering and processing NetFlow data to uncover valuable insights. This involves exporting flow records, managing large volumes of data, and integrating analytics tools for meaningful analysis.
Exporting Flow Records to Collectors
Exporting NetFlow data requires a well-coordinated setup between your network devices and collectors to ensure smooth performance and data accuracy. Routers and switches constantly generate flow records, and it's important to optimize how these records are exported to handle high traffic volumes while avoiding data loss.
Since NetFlow often uses UDP for data exports, packet loss can occur during network congestion. To reduce this risk, configure devices to send flow records to multiple destinations. This redundancy ensures that if one collector goes offline, the data can still reach another system. Many administrators use primary and secondary collectors located in different regions to maintain data visibility during outages.
Managing templates is another critical aspect, especially with protocols like NetFlow v9 or IPFIX, where template definitions are sent separately from flow data. Regularly resend templates to ensure collectors can correctly interpret the data, even after restarts or connectivity issues.
It's also essential to allocate enough buffer space on network devices to handle traffic spikes without losing flow records. Additionally, strike a balance with export timing - data should be sent promptly for visibility but without overloading system resources. Typically, flows are exported when they time out or when the flow cache fills up.
The next challenge is dealing with the large volumes of data generated, ensuring both performance and effective analysis.
Managing NetFlow Data at Scale
Large-scale networks, such as those with high-speed IP transit links, produce massive amounts of flow data - sometimes tens of thousands of records per minute during peak traffic. This creates a need for efficient storage and processing strategies.
To manage this data, consider real-time compression and aggregation. Grouping flows by source, destination, protocol, or time intervals can significantly reduce storage requirements.
Retention policies are equally important. One common strategy involves keeping detailed records for a short period to facilitate immediate troubleshooting while retaining aggregated summaries for long-term trend analysis.
As data grows, optimizing your database becomes critical. Time-series databases, designed for high-frequency data, often provide better compression and faster queries compared to traditional systems. Partitioning data by time intervals can further enhance performance and simplify tasks like archiving and deletion.
Storage systems must support high write speeds and handle the demands of concurrent queries. A combination of fast storage for recent data and cost-effective, high-capacity storage for archives can strike a good balance in meeting these demands.
Continuous data validation is vital in high-volume environments. Automated checks, such as verifying template availability, filtering out duplicate records, and ensuring timestamp accuracy, can help maintain data reliability. Regularly monitor collector metrics like processing rates and storage utilization to catch issues early.
Connecting NetFlow with Analytics Tools
To turn NetFlow data into actionable insights, it’s essential to integrate it with analytics tools. These tools allow for continuous monitoring and quick responses to anomalies in network traffic. However, successful integration requires careful attention to data formats, processing capabilities, and real-time needs.
Some tools support direct database connections to NetFlow collectors for real-time analysis, while others rely on periodic exports in formats like CSV or JSON. Choose the method that aligns best with your monitoring and reporting requirements.
Adding context to raw NetFlow data can make it even more useful. For example, integrating external data sources like DNS records, WHOIS information, or threat intelligence feeds can enrich IP addresses and domains with additional insights. Geographic data and autonomous system information can also help identify traffic patterns and network relationships.
Real-time streaming analytics take this a step further by enabling immediate responses to network events or security incidents. By processing flow data as it arrives, you can implement anomaly detection, threshold monitoring, and automated alerts. This capability is especially useful for identifying potential threats or routing problems quickly.
Custom dashboards can transform flow data into visual summaries tailored to different audiences. Network operations teams often need detailed, real-time graphs showing traffic and capacity trends. On the other hand, executives typically prefer high-level summaries that focus on overall performance and long-term trends.
As data volumes grow, optimizing analytics queries becomes increasingly important. Indexing key fields - like source and destination IPs, protocols, and timestamps - and pre-aggregating common metrics can greatly improve dashboard performance and reduce system strain.
Analyzing IP Transit Traffic Patterns and Performance
NetFlow data provides valuable insights by converting raw traffic records into actionable information. This helps identify bottlenecks and opportunities to fine-tune your network, directly influencing its efficiency.
Finding Traffic Trends and Anomalies
Start by pinpointing the "top talkers" - those consuming the most bandwidth - by sorting flows based on byte counts. This helps you quickly identify which users or applications are driving network activity.
To make traffic analysis more meaningful, compare current data with historical trends. For instance, if your network normally handles 2 Gbps during business hours but suddenly spikes to 5 Gbps, this anomaly signals the need for immediate attention. Such comparisons help establish baseline patterns, making it easier to detect irregularities.
Take it a step further with protocol analysis. If certain protocols show unexpected growth, it could signal underlying network issues. Additionally, analyzing geographic traffic patterns using IP geolocation can reveal routing inefficiencies that may be increasing latency or costs.
Application-level visibility is another key factor. NetFlow data can show which applications are consuming the most bandwidth, allowing you to make informed decisions about prioritizing traffic and adjusting network configurations. These insights ensure better performance and security.
With this data in hand, set up continuous monitoring and alert systems to catch anomalies quickly and take timely action.
Setting Up Monitoring and Alerts
Effective monitoring starts with configuring your data collection parameters the right way.
"Active timeouts should ALWAYS be set to 1-minute intervals (60 seconds in MLS and NX-OS). This value is the amount of time the device will flush the cache of any information pertaining to active flow conversations, and will ensure accurate trend and alarm information." - Julio E. Moisa, VIP Alumni, Cisco Community
This 60-second timeout ensures that your monitoring tools receive frequent updates, making alerts both timely and reliable.
For complete visibility, enable NetFlow on all Layer 3 interfaces across your infrastructure. As Julio E. Moisa emphasizes:
"Enable NetFlow on EVERY layer-3 interface for complete visibility." - Julio E. Moisa, VIP Alumni, Cisco Community
However, be strategic in how you configure it:
"NetFlow should be enabled for ingress traffic at the interface only; providing both ingress and egress statistics will effectively double the amount of reported bandwidth for an existing flow and is unnecessary in most cases." - Julio E. Moisa, VIP Alumni, Cisco Community
Once monitoring and alerts are in place, summarize key metrics in tables to make analysis quicker and more actionable.
Using Tables for Traffic Analysis
Tables are an effective way to present critical metrics, such as top talkers:
Tables like this highlight key traffic patterns, such as which IPs are consuming the most bandwidth, the protocols involved, and the duration of flows. Additionally, protocol distribution and performance comparison tables can reveal shifts over time and potential issues in different network segments. Focus on metrics that drive decisions, such as percentage changes or time-based trends, to complement your anomaly detection and alert systems.
For stable and reliable NetFlow monitoring, follow these best practices:
"It is best to source NetFlow export from an interface that will never go down, such as Loopback0." - Julio E. Moisa, VIP Alumni, Cisco Community
"Configure the NetFlow export version to 9 for flexibility and extensibility, as it uses definable record types and self-describing templates for easier collection engine configuration." - Julio E. Moisa, VIP Alumni, Cisco Community
Using NetFlow Data for Network Improvements
NetFlow data transforms raw network statistics into actionable insights, helping enhance performance, security, and operations. Let’s dive into how you can use these insights to optimize your network, strengthen security, and refine hosting strategies.
Improving Network Performance
NetFlow data offers a detailed view of network flow records, making it easier to spot routing inefficiencies. For instance, it can highlight asymmetric routing problems where traffic takes inefficient paths, leading to higher latency and wasted bandwidth.
With granular traffic visibility, real-time capacity adjustments become a reality. This lets you allocate resources effectively, avoiding over-provisioning while ensuring enough capacity during busy periods.
NetFlow insights also make traffic shaping and Quality of Service (QoS) policies more effective. By identifying which applications consume the most bandwidth and when, you can prioritize critical services. For example, if video conferencing peaks in the morning while file transfers dominate overnight, you can adjust QoS to ensure smooth real-time communication during business hours.
Another area where NetFlow shines is load balancing. It reveals whether traffic is evenly distributed across links or if some paths are underutilized. With this data, you can tweak routing policies to make the most of your infrastructure.
Finally, NetFlow data aids in network segmentation. By analyzing communication patterns between segments, you can fine-tune VLAN configurations and routing policies, reducing unnecessary traffic that may cause bottlenecks.
Improving Security and Incident Response
NetFlow data is a valuable tool for monitoring network security, offering behavioral insights that traditional security systems often miss. Instead of focusing on packet content, it uncovers communication patterns that might indicate malicious activity.
For example, DDoS attacks become evident through sudden spikes in flow records from numerous sources targeting specific destinations. This allows for quicker responses and better mitigation.
NetFlow also helps detect lateral movement within your network by identifying unusual communication between hosts. This type of anomaly detection often catches threats that signature-based systems overlook.
When it comes to data exfiltration, NetFlow data can flag unusual outbound traffic, such as large file transfers to unfamiliar destinations, particularly during off-hours. Comparing these patterns against baseline traffic helps identify potential breaches.
Forensic investigations benefit greatly from NetFlow’s historical data. If an incident occurs, the records provide a detailed timeline of network activity, helping you reconstruct the attack and pinpoint compromised systems. This is crucial for determining the scope of an attack and implementing effective remediation.
NetFlow data also supports compliance efforts. Many regulatory frameworks require detailed network activity monitoring, and NetFlow’s flow records and retention capabilities make meeting these requirements much easier.
Using NetFlow Data for Hosting Solutions
NetFlow isn’t just about security - it’s also a game-changer for hosting providers looking to improve operational efficiency.
By using NetFlow data, hosting providers can present customers with accurate bandwidth usage and performance metrics based on real flow records. This ensures precise, usage-based billing that reflects actual consumption rather than estimates.
When performance issues arise, network troubleshooting becomes faster and more targeted. NetFlow pinpoints specific flows, protocols, or sources causing congestion, eliminating the need for broad and time-consuming analyses.
Multi-tenant environments particularly benefit from NetFlow’s ability to track traffic by customer or application. This ensures fair resource allocation and helps quickly identify tenants or services impacting shared infrastructure.
For providers like FDC Servers, with 70+ locations worldwide, NetFlow data is invaluable. It optimizes traffic routing between data centers, ensuring customers experience consistent performance no matter their location. This level of visibility also enhances the management of unmetered dedicated servers and high-bandwidth services, enabling better capacity planning and performance tuning.
NetFlow data even supports predictive maintenance. By spotting gradual changes in traffic patterns, it can signal potential hardware issues or capacity constraints before they become critical. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and helps maintain the high availability customers expect.
Lastly, NetFlow enables custom reporting, giving customers detailed traffic analytics. This transparency builds trust and helps customers make informed decisions about scaling their infrastructure to meet future needs.
Conclusion: NetFlow and IP Transit Analysis Summary
NetFlow plays a key role in managing IP transit traffic, transforming raw data into meaningful insights that drive better decision-making. Here's a closer look at its value and how it integrates with modern infrastructure.
NetFlow Benefits for IP Transit Summary
NetFlow offers powerful advantages in optimizing network performance, bolstering security, and ensuring reliability. By providing detailed visibility into traffic patterns, it helps network managers identify bottlenecks, underutilized resources, and heavy bandwidth users. This enables smarter decisions for improving performance and allocating resources effectively.
On the security front, NetFlow shines by detecting anomalies and potential threats that traditional tools might overlook. For example, it’s particularly adept at spotting Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks by identifying unusual traffic spikes targeting specific resources.
The technology’s real-time monitoring capabilities allow for proactive issue resolution, minimizing downtime and improving user experience. Additionally, its historical data proves invaluable in tracing the origins and progression of incidents, aiding in investigations and preventing future attacks.
NetFlow also supports long-term planning by tracking network growth and predicting future bandwidth needs. This ensures networks can scale efficiently without over-provisioning. For organizations navigating regulatory requirements, NetFlow provides detailed activity logs that simplify compliance with monitoring mandates.
As highlighted earlier, these insights are critical for monitoring, troubleshooting, and planning network resources. Perhaps best of all, NetFlow is a cost-effective solution that leverages existing network infrastructure, making it accessible to organizations of all sizes without requiring significant hardware investments.
How FDC Servers Supports NetFlow Analysis
FDC Servers provides a global infrastructure designed to maximize the benefits of NetFlow analysis. With over 70 locations worldwide, its distributed architecture enables effective traffic monitoring and analysis on a large scale.
The company’s unmetered dedicated servers, starting at $129 per month, eliminate concerns about bandwidth limits, allowing organizations to collect comprehensive flow data without worrying about additional transfer costs. This ensures detailed traffic analysis without compromise.
FDC Servers also offers IP transit services with 10, 100, and 400 Gbps options, delivering the high-bandwidth connectivity required for seamless NetFlow data export and collection. The flexible pricing structure supports varying data volumes, making it easy to scale as monitoring needs grow.
With instant server deployment and customizable configurations, FDC Servers simplifies the setup of NetFlow collectors while ensuring optimal performance for data processing workloads. Around-the-clock support ensures uninterrupted operations, providing expert assistance whenever needed.
FAQs
How does NetFlow help detect and prevent security threats like DDoS attacks?
NetFlow serves as a critical tool for spotting and addressing security threats, including DDoS attacks. By examining traffic patterns, it can identify irregularities, such as abrupt surges in traffic or suspicious activity from certain IP addresses - classic signs of an attack.
When such activity is detected, NetFlow empowers security teams to respond swiftly with measures like traffic filtering or blackholing. These actions prevent the network from being overloaded, ensuring it remains stable and accessible. Its capacity to deliver detailed traffic insights makes NetFlow indispensable for staying ahead of potential threats and maintaining network security.
What are the best practices for configuring NetFlow in high-bandwidth networks to ensure smooth performance?
To get the most out of NetFlow in high-bandwidth networks, it’s crucial to focus on critical traffic. Implementing QoS policies and traffic shaping ensures that vital services run smoothly, even during peak usage, by reducing congestion.
Adjust active flow timeouts to 1-minute intervals. This strikes a balance between gathering useful data and avoiding unnecessary strain on your network resources. Also, keep NetFlow export bandwidth usage below 0.5% of your total network bandwidth to maintain stability across the network.
Lastly, pay close attention to how you configure flow sampling and export settings. Properly tuned settings allow for thorough monitoring without putting undue pressure on your infrastructure. By following these steps, you can effectively monitor IP transit traffic while keeping network performance intact.
How can using NetFlow with analytics tools improve network monitoring and incident response?
Integrating NetFlow data with analytics tools gives you a powerful edge in monitoring your network and tackling incidents effectively. NetFlow provides detailed insights into network traffic, making it possible to spot unusual behavior, study traffic trends, and pinpoint the root cause of any issues with precision.
With these insights at your fingertips, you can identify potential threats, address problems more quickly, and improve the overall stability and performance of your network. This proactive method helps keep your network secure and running smoothly.

How to install and use Redis on a VPS
Learn how to install and configure Redis on a VPS for optimal performance, security, and management in your applications.
9 min read - January 7, 2026
Monitoring your Dedicated server or VPS, what are the options in 2025?
12 min read - November 28, 2025

Have questions or need a custom solution?
Flexible options
Global reach
Instant deployment
Flexible options
Global reach
Instant deployment